- HOME
- Know Your Tech
- Data workflow management: What it is and why it matters
Data workflow management: What it is and why it matters
- Last Updated : January 27, 2026
- 4 Views
- 10 Min Read
Are your reports consistently delayed? Do team members work with different versions of the same data? These issues signal more than inefficiency; they point to disorganized data flows that slow decisions and create quality problems.
Data workflow management provides structure for how data moves through your business. It defines the path from collection to insights, reducing manual coordination and improving reliability. As operations scale, having clear workflows becomes essential.
This blog post covers data workflow management fundamentals in detail. You'll learn what it is, common workflow types, core components, implementation basics, and how businesses apply these concepts to solve real operational challenges.
Highlights
- Data workflow management defines how data moves through collection, processing, and delivery steps in your business.
- Structured workflows reduce manual coordination, improve data quality, and speed up decision-making.
- Common workflow types include integration, transformation, cleansing, analysis, machine learning, governance, and business intelligence workflows.
- Every workflow has five core components: sources, processing steps, a logic layer, outputs, and the people and tools that run it.
- Visual mapping reveals bottlenecks, redundancies, and dependencies that text descriptions miss.
What is data workflow management?
Data workflow management refers to how you design, control, and monitor the steps data follows inside your business. It includes how data is collected, cleaned, processed, and delivered to the right people or systems.
This process often involves both humans and automation. For example, a sales update might trigger a report, which then feeds into a dashboard your manager reviews daily. Each step is part of a defined flow.
Different teams use workflows for different goals. Some focus on cleaning messy data. Others aim to deliver insights without doing repetitive tasks. At least 68% of employees face a heavy workload due to daily repetitive work, which leads to lower productivity.
The structure and intent behind each workflow shape how it's designed and managed. Understanding these variations helps you plan more effectively and avoid mistakes.
Types of data workflows
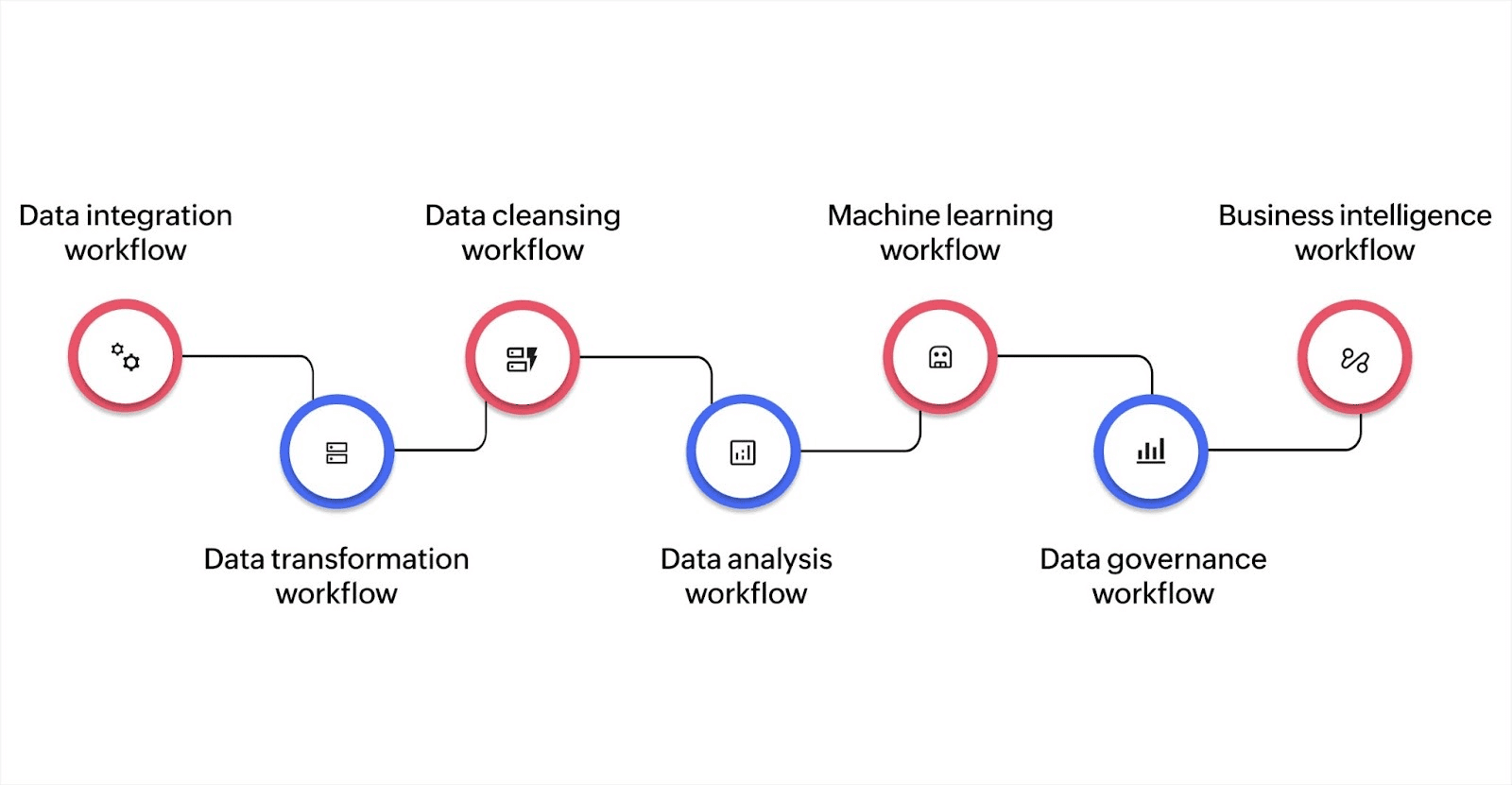
Workflows vary by business goal and data use case. Here are the most common types and how they function:
Data integration workflow
This workflow consolidates data from multiple sources, such as spreadsheets, customer databases, or marketing platforms, into a single location. It uses tools called application programming interfaces (APIs), which let different systems exchange data automatically. For example, you might retrieve order details from your online store with this workflow.
Data transformation workflow
Here, the goal is to convert data into the right format or structure for analysis. For example, you can convert a CSV file into JSON with this workflow.
This type also includes reshaping tables, renaming columns, or breaking down combined values into usable parts.
Data cleansing workflow
Cleaning up raw data is critical to making it trustworthy. This workflow corrects errors, removes duplicates, and fills in missing details. For instance, it can catch spelling mistakes in product names or make sure phone numbers follow a consistent format. Clean data means fewer mistakes in reports or customer communications.
Data analysis workflow
This type prepares and organizes data to answer questions. It may include organizing sales records, filtering out irrelevant entries, and using charts or visual tools to spot trends. Some businesses also apply basic statistics to understand seasonality or customer behavior. These workflows help turn stored data into useful insights for decisions. A sample data analysis workflow follows a circular approach: identifying the question, gathering data, cleaning and preparing it, conducting exploratory data analysis (EDA), building and analyzing models, creating visualizations, and finally interpreting results and producing reports.
Machine learning workflow
For data-driven teams using predictive models, machine learning workflows prepare data for training algorithms. These workflows involve selecting relevant variables, splitting data into training and testing sets, and validating model accuracy.
This applies to advanced use cases like predicting customer churn, forecasting sales, or automating customer support responses. Most businesses don't need this workflow type unless they're building predictive capabilities. A machine learning workflow consists of nine essential phases: defining the problem, gathering data, preprocessing it (cleaning and transforming), creating features, selecting a model, training the model, evaluating its performance, deploying it, and continuously monitoring and maintaining it.
Data governance workflow
This workflow ensures data is used correctly and meets company or legal standards. It includes setting access rules, tracking changes (called data lineage), and applying privacy checks.
For example, customer contact data might be protected from being shared with teams that don’t need it. This workflow helps businesses stay compliant with data protection laws.
Business intelligence workflow
This type delivers information to decision-makers. It pulls together cleaned and structured data into dashboards or reports, helping leaders monitor performance and take timely action. For example, you might create a daily report showing key performance indicators (KPIs) like revenue, inventory levels, or support ticket volumes with this workflow.
Why do data workflows matter?
- Ensure consistency: Defined workflows reduce guesswork. Everyone follows the same process, so data stays accurate across teams.
- Cut down manual work: Automating routine steps like syncing or reporting saves time and reduces errors.
- Improve cross-team collaboration: Clear workflows help engineering, analytics, and business teams work together without confusion or delays.
- Enable speed and control: From powering dashboards to audit logs, workflows move data reliably, supporting insights, compliance, and machine learning.
Core components of a data workflow
A data workflow works like a relay system. Each stage passes data along, refining it until it’s ready for use. These are the core parts that make it work:
Sources
This is where your data comes from. Sources can include:
- APIs: Secure connections between software systems that automatically share data in real time
- Files (spreadsheets, CSVs, etc.): Files that store data in a plain-text table format, often exported from other tools
- Databases: Structured collections of data, often used to store customer records, sales data, or product inventories
A reliable workflow handles different types of sources and updates at scheduled times or instantly when new data is available.
Processing
Once the data enters your system, it must be prepared before use. This step includes:
- Cleaning: Fixing errors, removing duplicates, and handling missing values
- Transforming: Converting data formats, such as changing a CSV file to a structured table or reorganizing the layout
- Integrating: Combining data from different sources into one place
- Validating: Making sure the data meets set standards or rules, like checking that email addresses are in the right format
Logic layer
This is where decisions are built into the workflow. It includes:
- Conditions: Rules like “if sales drop below $10,000, flag the data”
- Triggers: Automated actions that start the next step, like sending an email when a form is submitted
- Decision points: Steps where the workflow branches based on the data, guiding it in different directions depending on the result
Outputs
Once processed, the data goes to its destination. Common outputs include:
- Dashboards: Visual panels that track key metrics in real time
- Reports: Periodic summaries for teams to review
- Alerts: Notifications when data meets certain criteria
- Model outputs: Results generated by machine learning tools used for forecasting or recommendations
People and tools
A data workflow is powered by people and supported by tools:
- Engineers set up the technical structure.
- Analysts work on data, logic, and interpretation.
- Business users use the insights to make decisions.
- Workflow platforms help coordinate all these tasks. Some are low-code platforms, which means they let users build processes using visual drag-and-drop features instead of complex programming.
- Orchestration tools manage when and how different steps run. This ensures that tasks happen in the right order and at the right time.
Understanding each part of a data workflow gives you a strong foundation, but how do you bring it all together in practice? The next step is knowing how to design and implement the entire flow from start to finish.
How to build a data workflow
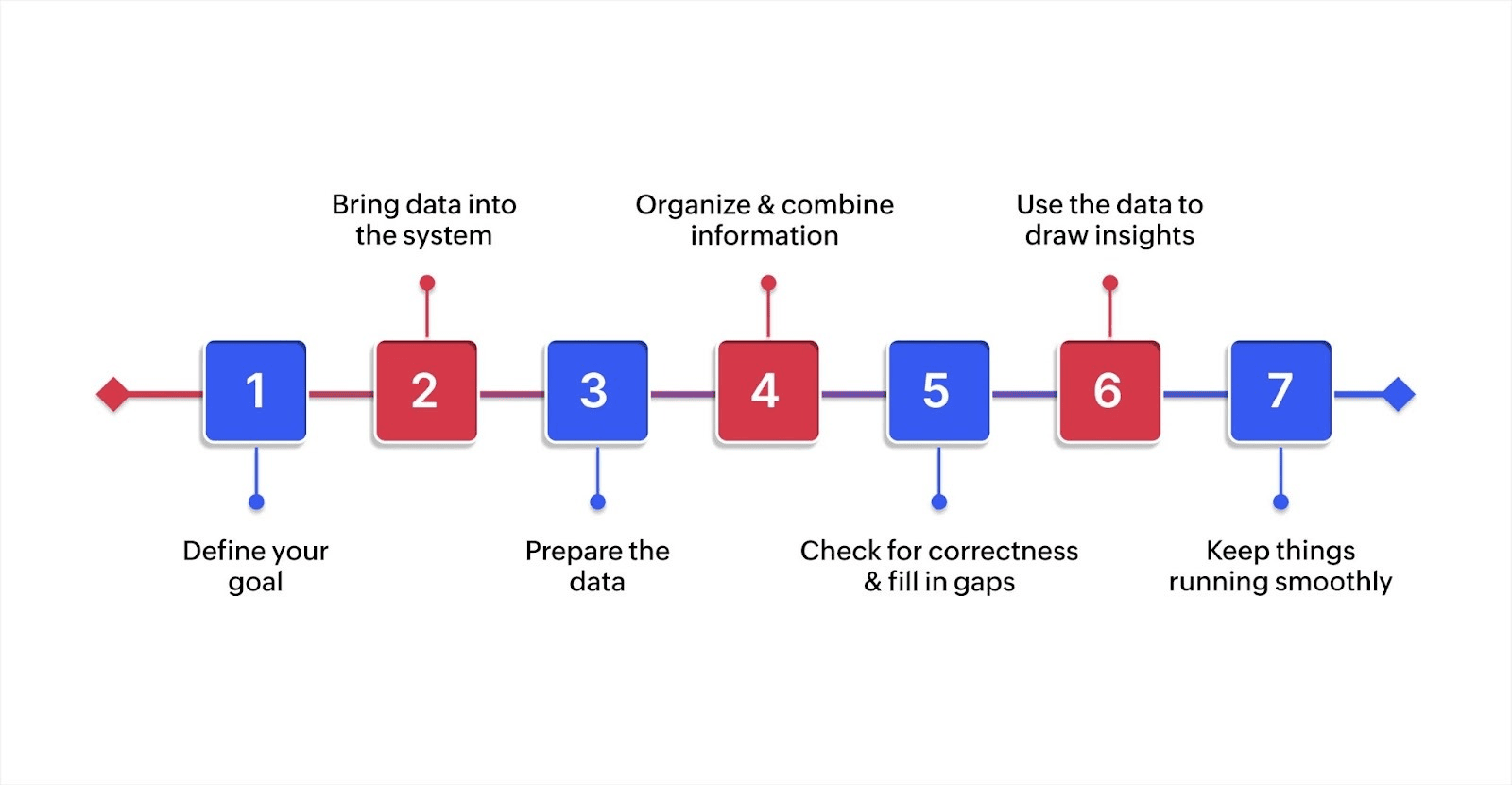
1. Define your goal
Begin with the outcome in mind. What decisions will this data support? From improving customer retention to optimizing marketing campaigns, make sure the purpose is defined and measurable.
It might be in spreadsheets, software platforms you already use, or tools your team relies on for daily tasks.
2. Bring data into the system
Extract the needed information from those sources and move it into your working environment. This can be done manually or automatically, depending on your setup.
3. Prepare the data
Check the data for errors, fix formatting issues, and remove duplicate or missing entries. This step ensures accuracy and consistency.
4. Organize and combine information
Bring together data from different places and reshape it to match your goal. For example, combine customer support records with sales data to understand user behavior better.
5. Check for correctness and fill in gaps
Run checks to confirm the data is trustworthy. Add helpful details if necessary, like converting time zones or calculating percentages.
6. Use the data to draw insights
Now that the data is structured and clean, analyze it. You might group customers by location, spot trends in spending, or compare this month’s numbers to the last.
7. Keep things running smoothly
A workflow isn’t “set it and forget it.” Check that everything continues to work as expected. If something breaks, fix it quickly so your team can continue making informed decisions.
Once your workflow is built, the next step is to make it visible. Seeing how each step connects helps everyone stay aligned and makes improvement easier.
Visualizing data workflows with diagrams
Visual mapping shows how data moves through each workflow stage. A diagram reveals the entire process on one page, making dependencies and bottlenecks obvious. When teams can see the complete flow, they understand how their work connects to other departments and where delays might occur.
Mapping helps you spot problems that text descriptions miss. You might find steps where data gets stuck waiting for manual approvals, redundant processes where multiple tools do the same work, or handoffs between teams that create unnecessary delays. These insights guide practical improvements rather than guessing where issues exist.
Several tools make creating diagrams straightforward. Lucidchart, Draw.io, and Miro work well for general workflow diagramming. You can use boxes for steps, arrows for data flow, and labels for decision points.
AI-powered low-code platforms like Zoho Creator include visual blueprint builders that let you map processes through drag-and-drop interfaces, define who handles each step, set conditions, and automate actions. The platform then helps you build the workflow based on your visual design.
Challenges in managing data workflows
At least 30% of enterprises are planning to automate over 50% of their workflow, so building workflows is just the start. Maintaining them, especially as your team, tools, and data grow, can get complex. Here are the most common issues businesses run into:
Data that doesn’t follow the rules
When incoming data is messy, incomplete, or inconsistent, it breaks processes down the line. Without checks at each stage, even one bad input can cause multiple errors.
Too many disconnected tools
You might collect data in one tool, change it in another, and report with a third. If these tools don’t connect well or require manual steps between them, errors and delays creep in.
Struggles with growing data
As your data scales, workflows that once worked can slow down or break. Systems not built for growth may lag, crash, or deliver outdated results.
Limited visibility into what's happening
Without clear tracking, it’s hard to know where a workflow is stuck or why a report didn’t update. Teams often rely on guesswork instead of real monitoring.
Compliance gaps
If your workflow lacks clear ownership or audit trails, you risk violating data protection rules. This gets riskier as regulations get stricter and more complex.
Facing workflow challenges often comes down to using the right tools that fit how your teams actually work.
Tools for building and managing workflows
From handling raw data to tracking task progress, each part of a workflow benefits from a focused tool. Here's how different platforms help, depending on what stage you're managing:
- To move and prepare data: Platforms like Talend and Informatica help you collect data from multiple sources, clean it, and prepare it for use. This stage, often referred to as "extract, transform, load," forms the foundation of most workflows.
- To manage flow and logic: If your workflow has multiple stages, tools like Apache Airflow and Prefect help organize and schedule those steps. These are useful when you're coordinating processes across teams or systems.
- To track workflow health: Monitoring platforms like Monte Carlo and Databand help you see where your workflow might be breaking down. They alert you when data isn’t updating or if something fails silently.
- To manage tasks and collaboration: When workflows involve people, not just data, platforms like Jira help track tasks, responsibilities, and progress. These tools are especially useful when your workflow ties into broader projects.
Tools like Cflow, Zapier, and Zoho Creator let non-developers create and manage workflows. With Zoho Creator, business users can build custom workflows, connect data, and automate reviews without writing complex scripts.
Now that you’ve seen the tools available, let’s look at how data workflows play out in real-world business functions. The value becomes clearer when you see what they solve for.
Use cases of data workflow management across industries
Data workflows aren’t just technical setups; they're useful enough to solve practical business problems across industries. Here are some typical use cases:
Customer onboarding in software companies
In SaaS businesses, workflows automate onboarding new customers, assigning customer success representatives, and triggering welcome emails. This ensures that every new customer receives a consistent and timely experience.
Real-time analytics in finance and telecom
Banks and telecom providers use workflows to process massive data streams in real time. These help detect fraud, track transactions, or optimize network usage. Data flows continuously from sensors or systems into analytics dashboards for immediate decisions.
Data governance in healthcare
Hospitals use workflows to manage how patient data is accessed and shared. From enforcing privacy rules to triggering compliance checks, these workflows ensure that sensitive health data stays protected.
Multi-platform marketing analytics
Marketing teams often pull data from platforms like Google Ads, email campaigns, and social media. Data workflows consolidate this information, clean it, and visualize performance across all channels so teams can adjust campaigns with clear, centralized insight.
Automate what matters with Zoho Creator
Data workflows are no longer managed by IT; they’ve become strategic tools for business agility, data governance, and cross-functional decision-making. As data volume and velocity grow, structured workflows give your teams a way to stay in control without losing speed or context.
Platforms like Zoho Creator simplify this transition. With its low-code approach, you can design, automate, and manage workflows across departments without needing deep technical skills. From dealing with compliance tracking to real-time analytics, Zoho Creator gives you the flexibility to build workflows.
Ready to build smarter workflows? Sign up for free today and turn scattered data into structured action.
FAQ
1. Why do businesses need data workflows?
They ensure consistent, reliable data use across teams, reduce manual effort, and make it easier to generate insights for decision-making.
2. How is a data workflow different from a single automated task?
A single task automation handles one action, while a data workflow connects several actions with logic and dependencies to achieve a complete process.
3. Can non-technical teams work with data workflows?
Yes. Many modern tools offer visual interfaces or templates that allow non-technical users to design and manage workflows without coding.
 Ann Elizabeth Sam
Ann Elizabeth SamHey! I'm Ann, and I work as a content writer at Zoho Creator. I'm exploring the SaaS world through various forms of content creation. Outside of work, I love dancing and would give up anything to read a good murder mystery.