- HOME
- All Topics
- Thought Leadership
- AI agents: What are they? Their types, and real-world applications
AI agents: What are they? Their types, and real-world applications
- Published : June 2, 2025
- Last Updated : June 11, 2025
- 866 Views
- 6 Min Read

Generative AI (GenAI) has changed the way we think about work. It’s smart, powerful, and able to process diverse information like text, voice, code, and more. AI agents take this capability further.
Imagine this: You wake up and your coffee is already brewed, your shower is preheated, and your car has already plotted the route for your meeting destination based on your calendar—all by itself. This is the future we're headed towards with AI agents.
What are AI agents?
AI agents are autonomous software that interact with its environment to gather data and make decisions using artificial intelligence to achieve specific goals. They require minimal to zero human intervention because they can reason with logic and data to make decisions and take actions.
They differ from AI assistants and bots because of their autonomy and the ability to learn, evolve, and make decisions without user input. They also work towards a certain goal set by systems or humans.
Key characteristics of AI agents
There are distinct characteristics that separate AI agents from the traditional AI assistants and bots.
For example, imagine a professor handing out an assignment.
Bots are students who follow the instructions line by line to complete the assignment.
AI assistants are the type of students who don't take initiative by themselves and require frequent inputs and course correction from the professor.
An AI agent is like a smart student who uses reasoning and excellent problem-solving skills to finish the assignment by themselves without any help from the professor.
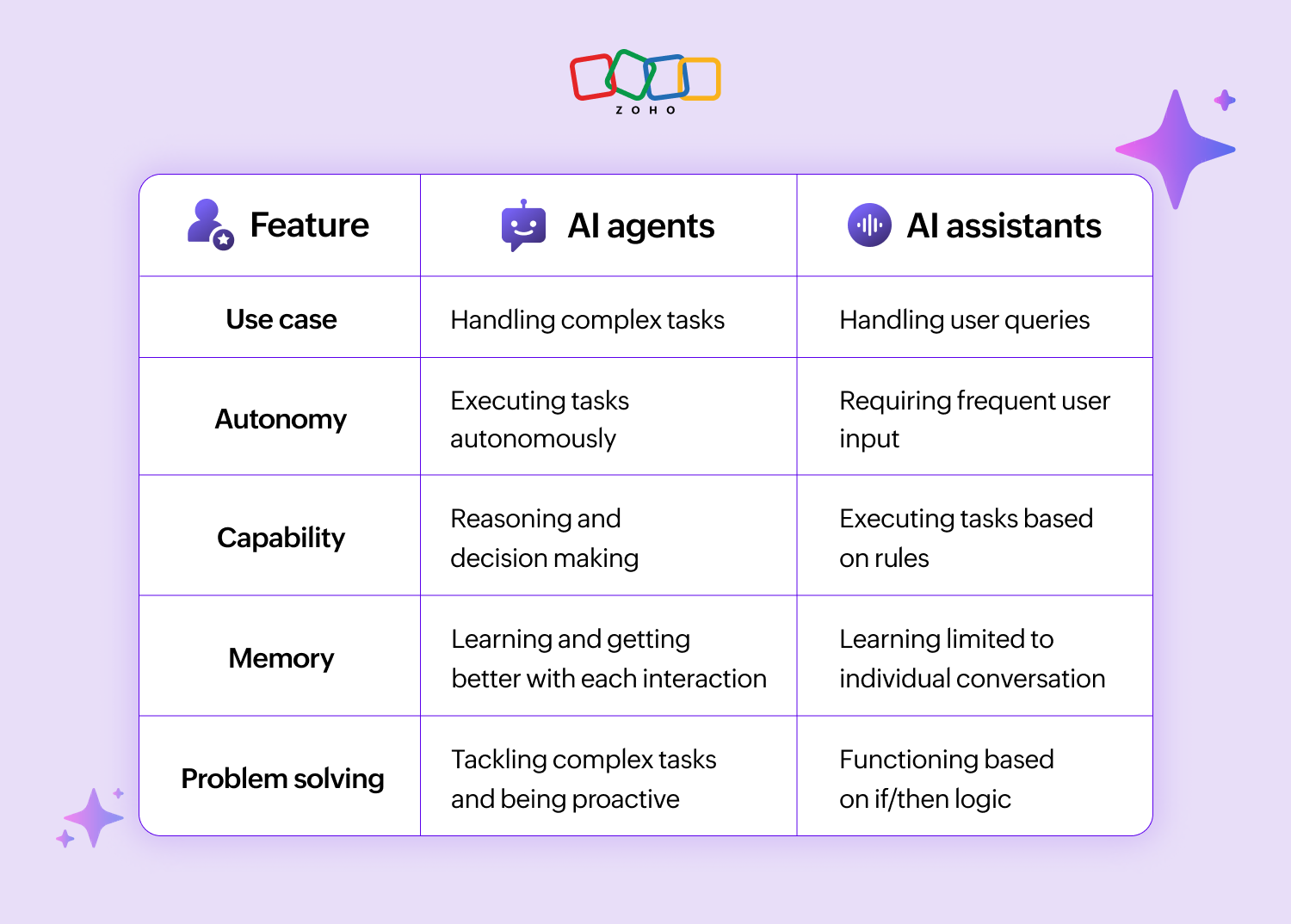
Autonomy: Takes action by themselves
A defining feature of AI agents is their ability to make decisions and execute them with minimal human intervention. They interact with the environment to collect data, reason with it, and take actions to achieve a predefined goal or objective set by the user.
Proactivity: Predicts problems well in advance
AI agents aren’t just reactive; they’re also proactive. They can store previous data in memory, analyze them, anticipate needs or potential problems, and address them well in advance. This can be highly beneficial in the logistics industry for predicting demands.
Learning: Learns and evolves with time
The ability to learn is another defining feature of AI agents. Each interaction with the environment allows these AI agents to learn, adapt, and evolve. This makes them more effective with time, enhancing their capabilities to solve complex tasks.
Reasoning: Does logical thinking with data
AI agents possess the ability to use logic and information they gather from the environment to reason and solve problems. This trait makes them highly effective in solving real-world issues and drawing conclusions.
Decision-making: Makes informed decisions
As we saw above, AI agents are capable of nuanced reasoning, so they can make informed decisions. The data from the environment lets them evaluate different options and come to an optimal decision that aligns with the goal.
Action-taking: Does the action based on its decisions
AI agents don't just stop with decision-making—they can also act on those decisions by executing actions autonomously. This is present in Tesla's Full Self-Driving (FSD) vehicles, where they analyze the environment, plan the route, and make decisions on which route to take.
Types of AI agents
There are different types of AI agents based on the task at hand, the data set they have access to, and the underlying architecture. Let's explore them.
Simple reflex agents: Agents without memory
The base form of AI agents has no memory of interactions or actions. These agents are primarily rules-driven, where they take inputs from the environment and react. An automatic door is a good example because it opens automatically when a person approaches.
Model-based reflex agents: Agents that know their environment
A slightly advanced version of AI agents maintains an internal model of the environment. This data allows them to analyze and make decisions. Robot vacuum cleaners use model-based reflex agents that map out the area, avoid obstacles, and keep the place clean.
Goal-based agents: Agents with a goal in mind
Goal-based agents work toward results by utilizing all of the data they have available from the environment. These agents possess excellent problem-solving skills to achieve their goals. Delivery robots use goal-based agents to plot the route, navigate, and make the delivery on time, ensuring customer satisfaction.
Utility-based agents: Agents that provide the most satisfaction
Sometimes, there will be multiple ways to achieve an objective. Utility-based agents shine here. They evaluate all variables, assign a value to them, and choose the one with the most utility. This increases the satisfaction level for the user. For example, users will be thrilled if their navigation system prioritizes a route optimizing for factors such as tolls, fuel efficiency, road conditions, and traffic.
Learning agents: Agents that learn and get better with time
Learning agents are constantly evolving from their experience to enhance their performance. Using machine learning techniques, they update their knowledge and refine decision-making. Autonomous robots working in warehouses can update their memory based on the changing environment and navigate accordingly.
Multi-agent systems: Multiple agents that form a hierarchy
Think of multi-agent systems as a fleet of powerful AI agents, collaborating within themselves, making individual decisions and actions to achieve a common goal. They form a hierarchy among themselves. For example, logistics agents can manage the fleet, choose destinations, and drive the trucks by themselves based on their goals.
Fundamental components of AI agents
As we saw above, AI agents are competent and powerful. They’re autonomous, self-driven, and goal-oriented. Now let's dive deep into the various components that make them smart and proficient.
Perception system: Gathers data from the environment
One of the key characteristics of AI agents is their ability to perceive the environment and gather data. The agents’ perception system makes this possible. The data includes inputs from computer vision, voice, and natural language processing.
Knowledge base: Stores historical data
AI agents also possess a knowledge base where they store historical data. This serves as their memory for making decisions, learning their environment, and refining their capabilities. The data in the knowledge base is stored based on domain and relevance.
Reasoning engine: Acts as the core intelligence
AI agents use their reasoning engine to analyze data, identify possible actions, and manage uncertainties. The reasoning engine serves as the core intelligence from which the agents draw their logical thinking capabilities.
Decision-making module: Makes decisions after reasoning
Decision-making is another highlighting feature of AI agents. This is possible with the decision-making module. The output from the reasoning engine is processed by the agents to make actionable decisions.
Action execution system: Translates decisions into actions
AI agents are also capable of making actions autonomously with the help of the action execution system. This system translates inputs from the decision-making module into actions. This also enables the agents to coordinate software with hardware as needed to achieve their goals.
Learning system: Learns from previous interactions
This is particular for learning agents alone. The learning system takes feedback from the environment to update its knowledge base. This lets it fine-tune the quality of decisions it makes over time and gets better with each interaction.
Real-world applications
AI agents and their capabilities may sound gimmicky on paper. But they have real-world impact that'll change the way humans work in the future. Let's explore some of them.
Customer support: Support agents who are available 24/7
For any organization, customer satisfaction is a priority. For customers, prompt response from the support is crucial. Both are made possible by AI agents. These are available 24/7, unlike humans, and help with support queries and personalized suggestions. This enhances customer experience and organizational efficiency by handling multiple interactions simultaneously.
Healthcare: Analyzes patterns for early disease discovery
AI agents are also advancing the healthcare space with their capabilities. They provide faster diagnosis by analyzing medical charts, automating routine admin tasks, helping patients with virtual medical assistance, and more. They’re also aiding in drug discovery and development for terminal illnesses like cancer.
Logistics: Predicts demand and prevents bottlenecks
Multi-agent systems are making logistics more efficient by predicting demand based on past trends and acting proactively to stock up. Goal-based agents plot delivery routes and schedules for a smooth overall operation.
Business operations: Frees human resources for creative tasks
AI agents can take up routine tasks and free human resources for more creative tasks. This lets employees focus on complex and strategic endeavors that require more thinking and strategy. Agents can also be used for crafting business briefings by combining data from multiple sources like a CRM and a document.
Security: Constantly monitors IT systems for cyberattacks
Security admins in organizations are bound to have a hard time staying on top of ever-evolving cyber threats. This is where AI agents can be helpful. They can analyze trends, spot vulnerabilities, and detect threats well in advance. They also act on fixing them and creating a security response framework without human input.
Transportation: Autonomous transport made possible
Driving is slowly becoming autonomous. Waymo and Tesla are already using AI agents to create self-driving vehicles. They use goal-based and utility agents to plot the most efficient route, navigate unpredictable traffic, and reach the destination on time. The decision-making module also lets them make split-second changes to avoid obstacles.
Wrapping up
AI agents are the next big thing, ushering in an era of efficient workplaces. These are smart and autonomous and can free up the workload of humans from trivial routine tasks.
What's the thing about AI agents that you're most excited about? Let us know in the comments below!
 Rohan
RohanRohan Samuel is a product marketer for Zoho Workplace who talks about workplace security, productivity, and collaboration. He is a highly enthusiastic writer who delights in evoking visual imagination with words. He also enjoys playing football with his buddies and traveling to new places.


